Details
Typical components & applications
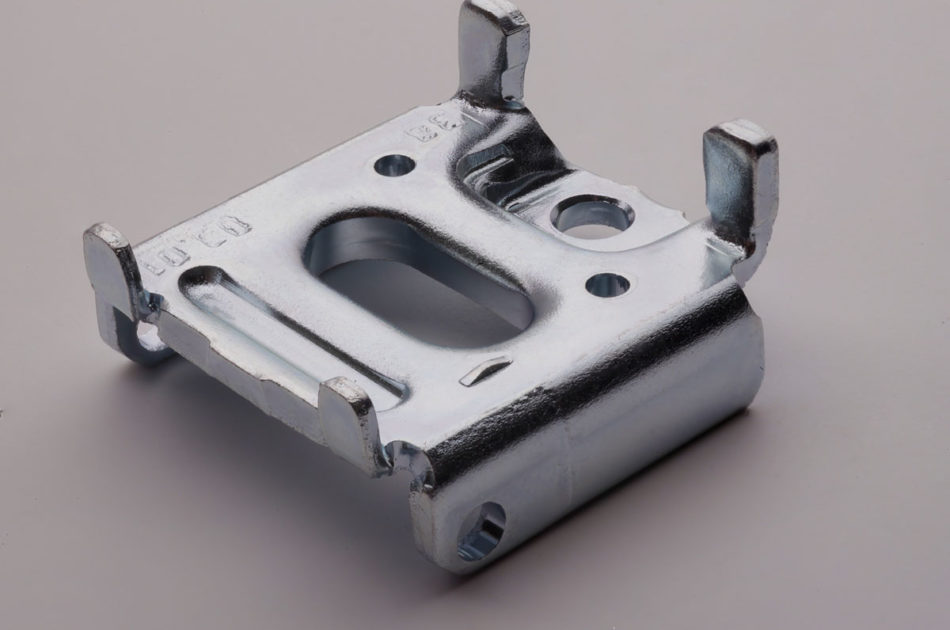
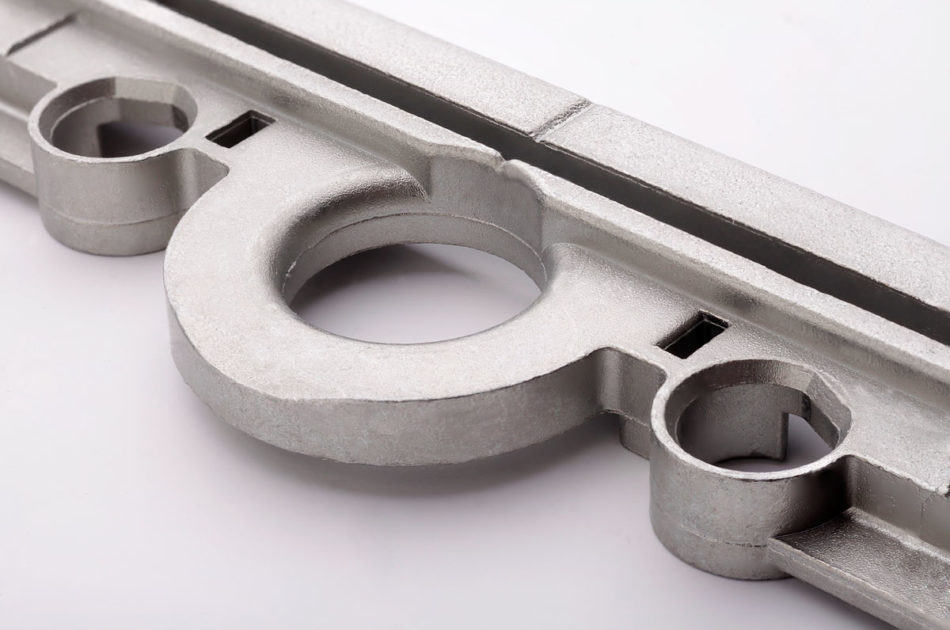
Typical components
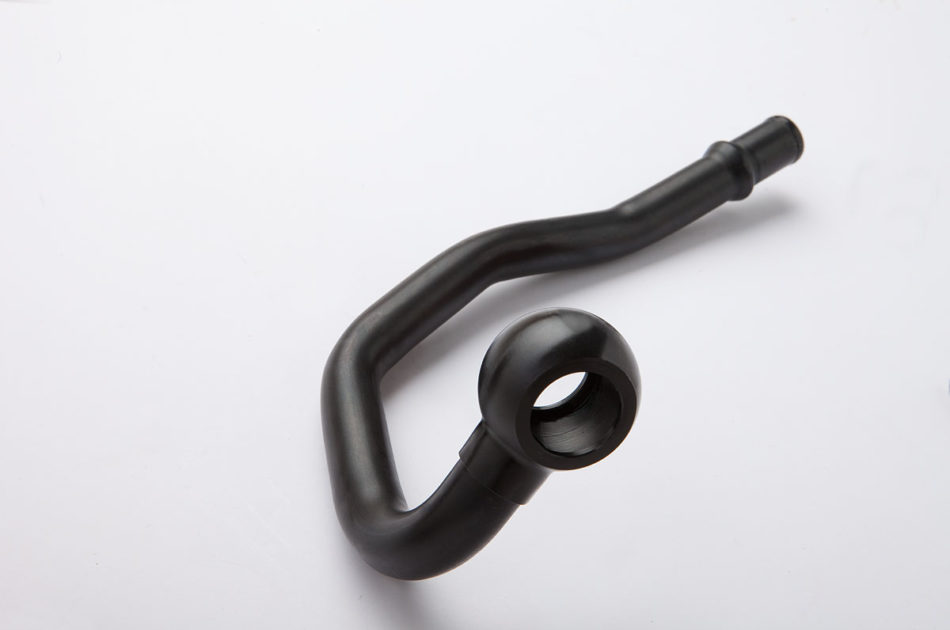
Components for: Drives, internal combustion engines (ZnNi), chassis, brakes, steering, pipes and hoses, pipe connections, fittings, screws, nuts, bolts, hose connections, fastening components
Industrial applications
Automotive, commercial vehicles, the hydraulic industry, mechanical engineering, connection components, the construction industry, the furniture industry
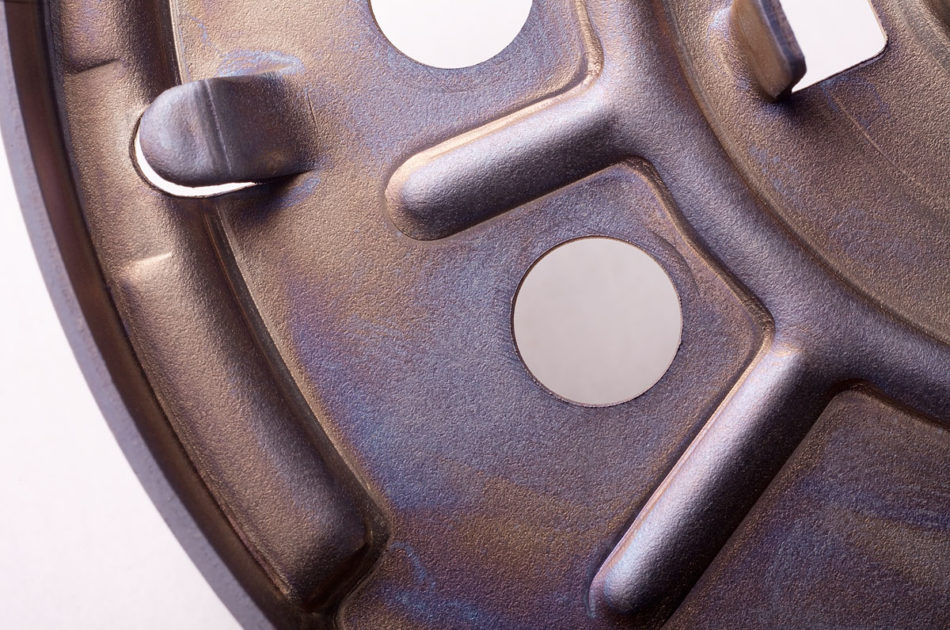
Zinc surfaces in the portfolio
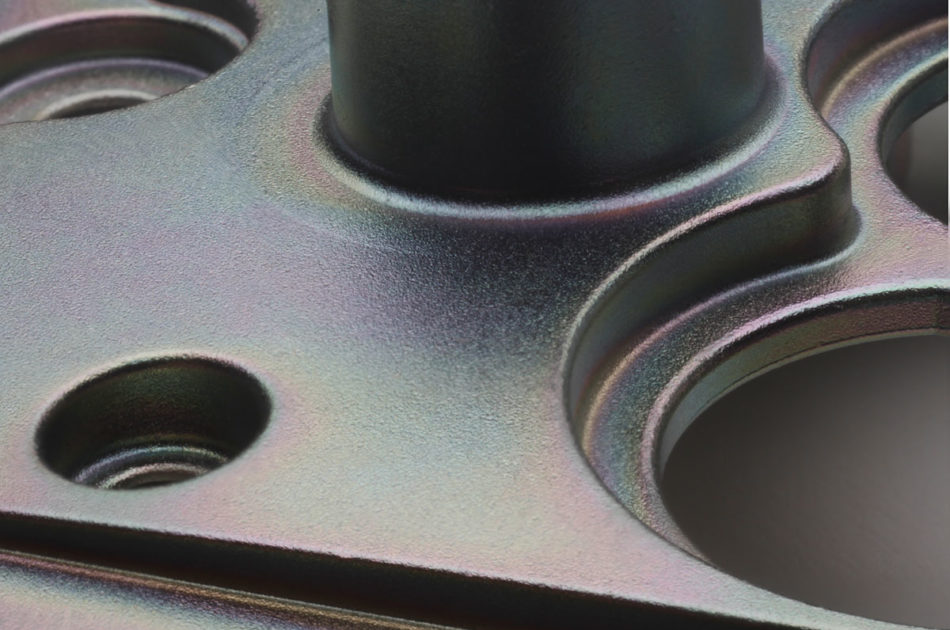
Zinc
Galvanic zinc coatings are used for the cathodic corrosion protection of steel and zinc die-cast components. The zinc coating dissolves first, thereby protecting the component against corrosive attacks. Corrosive attacks on the zinc surface can be greatly slowed down through the use of targeted post-treatments.
Galvanic zinc is deposited using acidic or alkaline electrolytes. The layer thicknesses are usually between 8 and 15 µm. The gloss level of the surface can be adjusted from matt to glossy by adding organic substances. The zinc coatings are so ductile that they can generally be deformed with the base material, but this diminishes somewhat when a very high gloss level is used.
After galvanisation, passivation is usually carried out to improve the corrosion protection of the galvanised surfaces. In passivation, there is a distinction between chromate coating and chromiumVI-free passivation systems.
Zinc-iron
Zinc-iron is a zinc alloy with an iron (Fe) content of 0.3% to 1%, which is characterised by high resistance to environmental influences. The zinc-iron alloy has improved corrosion resistance values compared to traditional galvanic coating, and with the corresponding passivations, deep black layers can be deposited. This means that zinc-iron is a technically better alternative for black surfaces in comparison to CDC and powder coating, as it also has a cathodic protective effect. Under corrosive stress, a firmly adherent, greyish oxide film forms on the surface, which cannot be removed.
Zinc-iron surfaces typically have layer thicknesses of 8 µm to 10 µm. These layers easily reach 480 h in the salt spray test against red rust.
Depending on the decorative specifications, the zinc-iron surface can be passivated in metallic silver-grey or black. Subsequent treatment with lubricant or sealant can be done. The adhesion of paints to zinc-iron is excellent.
Hydrogen embrittlement through the coating process can be prevented by subsequent heat treatment, which means that this process is also suitable for high-strength steel grades.
Zinc-nickel
Zinc-nickel is a zinc alloy with a Ni content of 12% to 15%. The zinc-nickel alloy ideally combines the corrosion inhibiting properties of zinc and nickel and provides very high resistance to environmental influences and weakly acidic media. Zinc-nickel surfaces typically have layer thicknesses of 5 µm to 10 µm. These layers easily achieve 720 h in the salt spray test against red rust, thereby complying with all current standards in the automotive industry. The removal rates in the corrosion test are approx. 1/10 of the removal rates of pure zinc layers. Therefore, depending on the layer thickness, significantly higher levels of corrosion resistance (>720 h) are possible. Zinc-nickel coatings are resistant to corrosion at temperatures up to 180 °C and are therefore also suitable for components in internal combustion engines where pure zinc coatings fail. For applications in which subsequent reshaping of the steel substrate is planned (e.g. straight pipes that will be reshaped), the special ductile variant Ductalloy® can be used. Even at the reshaped points, corrosion resistance of 720 h against red rust is achieved.
Zinc-nickel can be annealed by heat treatment. Zinc-nickel has the advantage of making this possible in the rational one-step process because the heat treatment has no negative impact on the passivation. Zinc-nickel is mainly used in components in the automotive industry, primarily in the engine and chassis area, areas with high corrosion stress. It is also used in commercial vehicles and in mechanical engineering and the hydraulics industry.